Lane Departure Warning System (LDWS) (Some Models)
The LDWS system notifies the driver that the vehicle may be deviating from its lane.
The system detects the white or yellow lines on the traffic lane using the Forward Sensing Camera (FSC) and if it determines that the vehicle may be deviating from its lane, it notifies the driver using the active driving display (vehicles with active driving display), and by flashing the LDWS warning light and activating the LDWS warning beep.
Use the LDWS when you drive the vehicle on roads with white or yellow lines.
Refer to Forward Sensing Camera (Search).
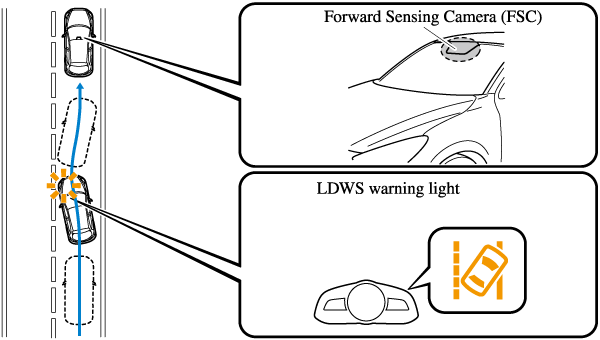
The warning light illuminates when the system has a malfunction.
Refer to Warning Lights (Search).
Do not use the LDWS under the following conditions:
The system may not operate adequately according to the actual driving conditions, resulting in an accident.
-
Driving on roads with tight curves.
-
Driving under bad weather conditions (rain, fog, and snow).
The functions of the LDWS have limitations:
Always stay on course using the steering wheel and drive with care. The system is not designed to compensate for a driver’s lack of caution and if you rely too much on the LDWS it could lead to an accident. The driver is responsible for assuring lane changes and other manoeuvres. Always pay attention to the direction in which the vehicle is travelling and the vehicle’s surroundings.


Do not modify the suspension. If the vehicle height or the damping force of the suspensions is changed, the LDWS may not operate correctly.


-
If your vehicle deviates from its traffic lane, the LDWS operates (warning sound and indicator light). Steer the vehicle adequately to drive the vehicle to the centre of the lane.
-
When the direction indicator lever is operated for a lane change, the LDWS warning is automatically cancelled. The LDWS warning becomes operable when the direction indicator lever is returned and the system detects the white or yellow lines.
-
If the steering wheel, accelerator pedal, or brake pedal is operated abruptly and the vehicle moves close to a white or yellow line, the system determines that the driver is making a lane change and the LDWS warning is automatically cancelled.
-
The LDWS may not operate during the period immediately after the vehicle has deviated from its lane and the LDWS has operated, or the vehicle deviates from its lane repeatedly within a short period of time.
-
The LDWS does not operate if it does not detect the white or yellow lines of the traffic lane.
-
Under the following conditions, the LDWS may not be able to detect white or yellow lines correctly and the LDWS may not operate correctly.
-
If an object placed on the instrument panel is reflected in the windscreen and picked up by the camera.
-
Heavy luggage is loaded in the luggage compartment or on the rear seat and the vehicle is inclined.
-
The tyre pressures are not adjusted to the specified pressure.
-
When the vehicle is driven on the entry and exit to or from the rest area or tollgate of a highway.
-
The white or yellow lines are less visible because of dirt or paint flaking.
-
The vehicle ahead is running near a white or yellow line and the line is less visible.
-
A white or yellow line is less visible because of bad weather (rain, fog, or snow).
-
The vehicle is driven on a temporary lane or section with a closed lane due to construction.
-
A misleading line is picked up on the road such as a temporary line for construction, or because of shade, lingering snow, or grooves filled with water.
-
The surrounding brightness suddenly changes such as when entering or exiting a tunnel.
-
The illumination of the headlights is weakened because of dirt or the optical axis is deviated.
-
The windscreen is dirty or foggy.
-
Back-light is reflecting from the road surface.
-
The road surface is wet and shiny after rain, or there are puddles on the road.
-
The shade of a guardrail parallel to a white or yellow line is on the road.
-
The width of a lane is excessively narrow or wide.
-
The road is excessively uneven.
-
The vehicle is shaken after hitting a road bump.
-
There are two or more adjacent white or yellow lines.
-
There are various road markings or lane markings of various shapes near an intersection.
-




 Read this first
Read this first










