i-ACTIVSENSE (Some Models)
Adaptive Front Lighting System (AFS) (Some Models)
High Beam Control System (HBC) (Some Models)
Lane Departure Warning System (LDWS) (Some Models)
Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM) System (Some Models)
Distance Recognition Support System (DRSS) (Some Models)
Rear Cross Traffic Alert (RCTA) (Some Models)
Mazda Radar Cruise Control (MRCC) (Some Models)
Adjustable Speed Limiter (Some Models)
Smart City Brake Support (SCBS) (Some Models)
Smart Brake Support (SBS) (Some Models)
Forward Sensing Camera (FSC) (Some Models)
Radar Sensor (Front) (Some Models)
Laser Sensor (Front) (Some Models)
Radar Sensors (Rear) (Some Models)
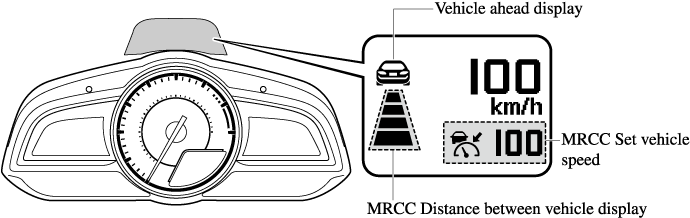
Mazda Radar Cruise Control (MRCC) Display Indication
The setting status and operation conditions of the Mazda Radar Cruise Control (MRCC) system are indicated in the active driving display.


 Read this first
Read this first










