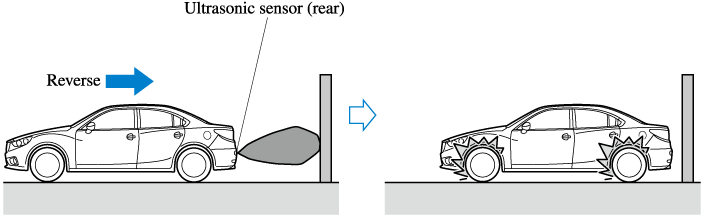
Smart City Brake Support [Reverse] (SCBS R) (Some Models)
Smart City Brake Support [Reverse] (SCBS) is a system which is designed to reduce damage in the event of a collision by operating the brake control (SCBS brake) when the system’s ultrasonic sensors detect an obstruction at the rear of the vehicle while driving at a speed of about 2 to 8 km/h (2 to 4 mph) and the system determines that a collision is unavoidable. In addition, when the driver depresses the brake pedal while the system is in the operation range at a vehicle speed of about 2 to 8 km/h (2 to 4 mph), the brakes are applied firmly and quickly to provide assistance. (Brake Assist (SCBS brake assist))
Do not rely completely on the Smart City Brake Support [Reverse] system:
-
The Smart City Brake Support [Reverse] (SCBS R) system is only designed to reduce damage in the event of a collision. Over reliance on the system leading to the accelerator pedal or brake pedal being mistakenly operated could result in an accident.
-
To assure the correct operation of the Smart City Brake Support [Reverse] (SCBS R), heed the following cautions.
-
Do not apply a sticker to an ultrasonic sensor (rear) (including transparent stickers). Otherwise, the ultrasonic sensor (rear) may not be able to detect vehicles or obstructions which could result in an accident.
-
Do not disassemble an ultrasonic sensor (rear).
-
If cracks or damage caused by flying gravel or debris is visible around an ultrasonic sensor (rear), stop using the Smart City Brake Support [Reverse] (SCBS R) system immediately and have your vehicle inspected by an expert repairer, we recommend an Authorised Mazda Repairer. If the vehicle continues to be driven with cracks or scratch marks left around an ultrasonic sensor, the system may operate unnecessarily and cause an unexpected accident.
Refer to Personalisation Features on how to turn off the system. (Search)
-
Consult an expert repairer, we recommend an Authorised Mazda Repairer for rear bumper replacement.
-
Do not modify the suspension:
If the vehicle height or inclination is changed, the Smart City Brake Support [Reverse] (SCBS R) system may not operate correctly because it cannot detect obstructions correctly.
Do not apply a strong force to an ultrasonic sensor (rear):
When washing the vehicle, do not spray highly pressurised water against an ultrasonic sensor (rear), or rub it strongly. In addition, do not hit the rear bumper forcefully when loading and unloading cargo Otherwise, the sensors may not detect obstructions correctly which could cause the Smart City Brake Support [Reverse] (SCBS R) system to not operate normally, or it could operate unnecessarily.


-
When driving off-road in areas where there is grass or forage, it is recommended that the Smart City Brake Support [Reverse] (SCBS R) system be turned off.
-
Always use tyres of the specified size and the same manufacturer, brand, and tread pattern on all 4 wheels. In addition, do not use tyres with significantly different wear patterns on the same vehicle. Do not use tyres with significantly different wear patterns on the same vehicle. Otherwise, the Smart City Brake Support [Reverse] (SCBS R) system may not operate normally.
-
If ice or snow is stuck on the ultrasonic sensors (rear) they may not be able to detect obstructions correctly depending on the conditions. In such cases, the system may not be able to perform controls correctly. Always drive carefully and pay attention to the rear of the vehicle.


-
The vehicle posture changes depending on the accelerator pedal, brake pedal and steering wheel operations, which could make it difficult for the system to recognise an obstruction, or it could facilitate unnecessary detection. In such cases, the Smart City Brake Support [Reverse] (SCBS R) may or may not operate.
-
The Smart City Brake Support [Reverse] (SCBS R) system will operate under the following conditions.
-
The engine is running.
-
The selector lever is in the R (reverse) position.
-
“SCBS Reverse malfunction” is not displayed in the multi-information display.
-
The vehicle speed is between about 2 to 8 km/h (2 to 4 mph).
-
The Smart City Brake Support (SCBS) is not turned off.
-
The DSC is not malfunctioning.
-
-
The Smart City Brake Support [Reverse] (SCBS R) operates using ultrasonic sensors (rear) which detect obstructions at the rear by emitting ultrasonic waves and then receiving the returning waves reflected off the obstructions.
-
In the following cases, the ultrasonic sensors (rear) cannot detect obstructions and the Smart City Brake Support [Reverse] (SCBS R) may not operate.
-
The height of the obstruction is low such as low walls or trucks with low loading platforms.
-
The height of the obstruction is high such as trucks with high loading platforms.
-
The obstruction is small.
-
The obstruction is thin such as a signpost.
-
The obstruction is positioned away from the centre of the vehicle.
-
The surface of the obstruction is not pointed vertically relative to the vehicle.
-
The obstruction is soft such as a hanging curtain or snow stuck to a vehicle.
-
The obstruction is shaped irregularly.
-
The obstruction is extremely close.
-
-
In the following cases, the ultrasonic sensors (rear) cannot detect obstructions correctly and the Smart City Brake Support [Reverse] (SCBS R) may not operate.
-
Something is stuck on the bumper near an ultrasonic sensor (rear).
-
The steering wheel is turned sharply, or the brake or accelerator pedal is operated.
-
There is another obstruction near one obstruction.
-
During inclement weather such as rain, fog and snow.
-
High or low humidity.
-
High or low temperatures.
-
Strong winds.
-
The path of travel is not flat.
-
Heavy luggage is loaded in the luggage compartment or on the rear seat.
-
Objects such as a wireless aerial, fog light, or illuminated number plate is installed near an ultrasonic sensor (rear).
-
The orientation of an ultrasonic sensor (rear) has deviated for reasons such as a collision.
-
The vehicle is affected by other sound waves such as the horn, engine noise, ultrasonic sensor of another vehicle.
-
-
In the following cases, an ultrasonic sensor (rear) may detect something as a target obstruction which could cause the Smart City Brake Support [Reverse] (SCBS R) system to operate.
-
Driving on a steep slope.
-
Wheel blocks.
-
Hanging curtains, gate poles such as at toll gates and railroad crossing.
-
When travelling near objects such as foliage, barriers, vehicles, walls, and fences along a road.
-
When driving off-road in areas where there is grass and forage.
-
When passing through low gates, narrow gates, car washing machines, and tunnels.
-
A towing bar is installed or a trailer is connected.
-




 Read this first
Read this first



















