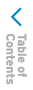
Passenger Occupant Classification Sensor
Your vehicle is equipped with a passenger occupant classification sensor as a part of the supplementary restraint system. This sensor is equipped in the passenger's seat cushion. This sensor measures the electrostatic capacity of the passenger's seat. The SAS unit is designed to prevent the passenger front and side air bags and seat belt pretensioner system from deploying if the passenger air bag deactivation OFF indicator light turns on.
To reduce the chance of injuries caused by deployment of the passenger air bag, the system deactivates the passenger front and side air bags and also the seat belt pretensioner system when the passenger air bag deactivation OFF indicator light turns on. Refer to the following table for the passenger air bag deactivation indicator light illumination conditions.
This system shuts off the passenger front and side air bags and seat belt pretensioner system, so make sure the passenger air bag deactivation indicator light turns on according to the following table.
The air bag/seat belt pretensioner system warning light flashes and the passenger air bag deactivation OFF indicator light illuminates if the sensors have a possible malfunction. If this happens, the passenger front and side air bags and seat belt pretensioner system will not deploy.
Passenger air bag deactivation indicator lights
These indicator lights turn on to remind you that the passenger front and side air bags and seat belt pretensioner will or will not deploy during a collision.
If the passenger occupant classification sensor is normal, both indicator lights turn on when the ignition is switched ON. The lights turn off after a few seconds. Then, the indicator lights turn on or off under the following conditions:
Passenger air bag deactivation indicator light on/off condition chart
|
Condition detected by the passenger occupant classification system |
Passenger air bag deactivation indicator light |
Passenger front and side air bags |
Passenger seat belt pretensioner system |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Empty (Not occupied) |
 |
Deactivated |
Deactivated |
|
A child is seated in a child-restraint system*1 |
 |
Deactivated |
Deactivated |
|
Adult*2 |
 Turns off after a short period of time. |
Ready |
Ready |
-
The occupant classification sensor may not detect a child seated on the seat, in a child-restraint system, or a junior seat depending on the child's physical size and seated posture.
-
If a smaller adult sits on the passenger seat, the sensors might detect the person as being a child depending on the person's physique.
If both of the passenger air bag deactivation indicator lights do not turn on for a specified period of time when the ignition is switched ON or they do not turn on as indicated in the passenger air bag deactivation indicator light on/off condition chart, do not allow an occupant to sit in the passenger seat and consult an Authorised Mazda Repairer as soon as possible. The system may not work properly in an accident.
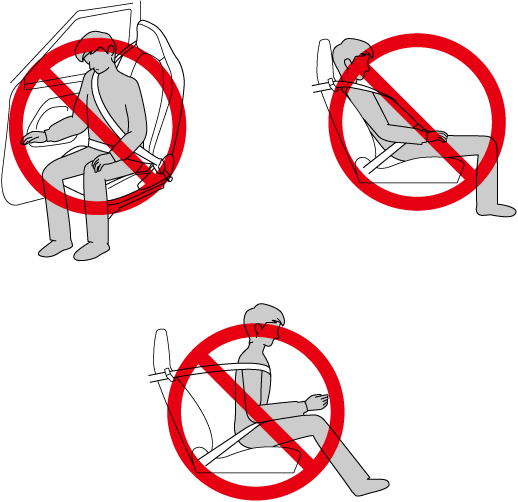
Do not allow an occupant in the passenger's seat to sit with a posture which makes it difficult for the passenger occupant classification sensor to detect the occupant correctly:
Sitting in the passenger's seat with a posture which makes it difficult for the passenger occupant classification sensor to detect the occupant correctly is dangerous. If the passenger occupant classification sensor cannot detect the occupant sitting on the passenger's seat correctly, the passenger front and side air bags and pretensioner system may not operate (non-deploy) or they may operate (deploy) accidentally. The passenger will not have the supplementary protection of the air bags or the accidental operation (deployment) of the air bags could result in serious injury or death.
Under the following conditions, the passenger occupant classification sensor cannot detect a passenger sitting on the passenger's seat correctly and the deployment/non-deployment of the air bags cannot be controlled as indicated in the passenger air bag deactivation indicator light on/off condition chart. For example:
-
A passenger is seated as shown in the following figure:
-
Luggage or other items placed under the passenger seat or between the passenger seat and driver seat that push up the passenger seat bottom.
-
An object, such as a seat cushion, is put on the passenger's seat or between the passenger's back and the seatback.
-
A seat cover is put on the passenger's seat.
-
Luggage or other items are placed on the seat with the child in the child-restraint system.
-
The seat is washed.
-
Liquids are spilled on the seat.
-
The passenger seat is moved backward, pushing into luggage or other items placed behind it.
-
Luggage or other items are placed between the passenger seat and driver seat.
-
An electric device is put on the passenger's seat.
-
An additional electrical device, such as a seat warmer is installed to the surface of the passenger seat.
The passenger front and side air bags and seat belt pretensioner systems will deactivate if the passenger air bag deactivation OFF indicator light turns on.
-
To assure proper deployment of the front air bag and to prevent damage to the sensor in the seat cushion:
-
Do not place sharp objects on the seat cushion or leave heavy luggage on them.
-
Do not spill any liquids on the seats or under the seats.
-
-
To allow the sensors to function properly, always perform the following:
-
Adjust the seats as far back as possible and always sit upright against the seatbacks with seat belts worn properly.
-
If you place your child on the passenger seat, secure the child-restraint system properly and slide the passenger seat as far back as possible within the position in which the child-restraint system can be installed.
-
-
The system requires about 10 seconds to alternate between turning the passenger front and side air bags and seat belt pretensioner system on or off.
-
The passenger air bag deactivation OFF indicator light may turn on repeatedly if luggage or other items are put on the passenger seat, or if the temperature of the vehicle's interior changes suddenly.
-
The passenger air bag deactivation OFF indicator light may turn on for 10 seconds if the electrostatic capacity on the passenger seat changes.
-
The air bag/seat belt pretensioner system warning light might turn on if the passenger seat receives a severe impact.
-
If the passenger air bag deactivation OFF indicator light does not turn on after installing a child-restraint system on the passenger seat, first, re-install your child-restraint system according to the procedure in this owner's manual. Then, if the passenger air bag deactivation OFF indicator light still does not turn on, and consult an Authorised Mazda Repairer as soon as possible.
-
If the passenger air bag deactivation OFF indicator light turns on when an occupant is seated directly in the passenger seat, have the passenger re-adjust their posture by sitting with their feet on the floor, and then re-fastening the seat belt. If the passenger air bag deactivation OFF indicator light remains turned on, slide the passenger seat as far back as possible. Consult an Authorised Mazda Repairer as soon as possible.




