Rear Cross Traffic Alert (RCTA) (Some Models)
The Rear Cross Traffic Alert (RCTA) system is designed to assist the driver in checking the area to the rear of the vehicle on both sides while the vehicle is reversing by alerting the driver to the presence of vehicles approaching the rear of the vehicle.
The Rear Cross Traffic Alert (RCTA) system detects vehicles approaching from the left and right sides of the vehicle while the vehicle is being reversed out of a parking space, and notifies the driver of possible danger using the Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM) warning indicator lights and the warning buzzer.
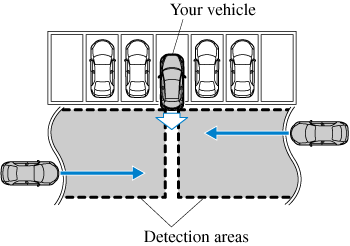
Rear Cross Traffic Alert (RCTA) operation
-
The Rear Cross Traffic Alert (RCTA) system operates when the shift lever (manual transaxle) or the selector lever (automatic transaxle) is shifted to the reverse (R) position.
-
If there is the possibility of a collision with an approaching vehicle, the Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM) warning indicator lights flashes and the warning beep is activated simultaneously.
(With rear view monitor)
The Rear Cross Traffic Alert (RCTA) warning indication in the rearview monitor also synchronizes with the Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM) warning indicator light on the door mirrors.

Always check the surrounding area visually before actually putting the vehicle in reverse:
The system is only designed to assist you in checking for vehicles at the rear when putting the vehicle in reverse. Due to certain limitations with the operation of this system, the Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM) warning indicator lights may not flash or it might be delayed even though a vehicle is behind your vehicle. Always make it your responsibility as a driver to check the rear.


-
In the following cases, the Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM) warning indication/warning light turns on and operation of the system is stopped. If the Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM) warning indication/warning light remains illuminated, have the vehicle inspected at an Authorised Mazda Dealer as soon as possible.
-
Some problem with the system including the Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM) warning indicator lights has occurred.
-
A large deviation in the installation position of a radar sensor (rear) on the vehicle has occurred.
-
There is a large accumulation of snow or ice on the rear bumper near a radar sensor (rear).
-
Driving on snow-covered roads for long periods.
-
The temperature near the radar sensors becomes extremely hot due to driving for long periods on slopes during the summer.
-
The battery voltage has decreased.
-
-
Under the following conditions, the radar sensors (rear) cannot detect target objects or it may be difficult to detect them.
-
The vehicle speed when reversing is about 10 km/h (6 mph) or faster.
-
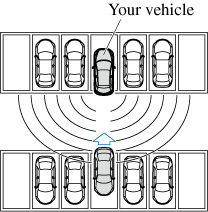
The radar sensor (rear) detection area is obstructed by a nearby wall or parked vehicle. (Reverse the vehicle to a position where the radar sensor detection area is no longer obstructed.)
-
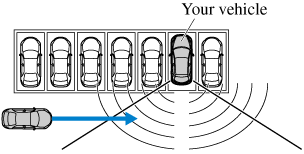
A vehicle is approaching directly from the rear of your vehicle.
-
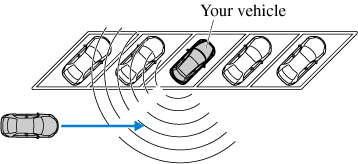
The vehicle is parked on a slant.
-
(With Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM) OFF switch)
Directly after pressing the Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM) OFF switch and the system becomes operable.
(Without Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM) OFF switch)
Directly after the Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM) system becomes operable.
-
-
In the following cases, it may be difficult to view the illumination/flashing of the Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM) warning indicator lights equipped on the door mirrors.
-
Snow or ice adheres to the door mirrors.
-
The front door glass is fogged or covered in snow, frost or dirt.
-
-
Turn off the Rear Cross Traffic Alert (RCTA) system while pulling a trailer or while an accessory such as a bicycle carrier is installed to the rear of the vehicle. Otherwise, the radio waves emitted by the radar will be blocked causing the system to not operate normally.




 Read this first
Read this first



















