i-ACTIVSENSE (Some Models)
Adaptive Front Lighting System (AFS) (Some Models)
High Beam Control System (HBC) (Some Models)
Adaptive LED Headlights (ALH) (Some Models)
Lane Departure Warning System (LDWS) (Some Models)
Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM) System (Some Models)
Traffic Sign Recognition System (TSR) (Some Models)
Distance Recognition Support System (DRSS) (Some Models)
Driver Attention Alert (DAA) (Some Models)
Rear Cross Traffic Alert (RCTA) (Some Models)
Mazda Radar Cruise Control (MRCC) (Some Models)
Adjustable Speed Limiter (Some Models)
Advanced Smart City Brake Support (Advanced SCBS) (Except Indonesia, Malaysia, and Thailand) (Some Models)
Smart City Brake Support [Forward] (SCBS F) (Indonesia, Malaysia, and Thailand) (Some Models)
Smart City Brake Support [Reverse] (SCBS R) (Some Models)
Smart Brake Support (SBS) (Some Models)
Forward Sensing Camera (FSC) (Some Models)
Radar Sensor (Front) (Some Models)
Radar Sensors (Rear) (Some Models)
Ultrasonic Sensor (Rear) (Some Models)
Ultrasonic Sensor (Rear) (Some Models)
The ultrasonic sensors (rear) function by emitting ultrasonic waves which are reflected off obstructions at the rear and the returning ultrasonic waves are picked up by the ultrasonic sensors (rear).
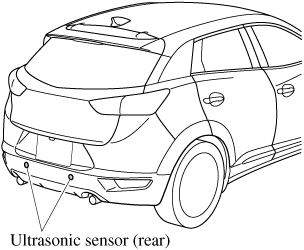
The ultrasonic sensors (rear) are mounted in the rear bumper.


 Read this first
Read this first



















