Traffic Sign Recognition System (TSR) (Some Models)
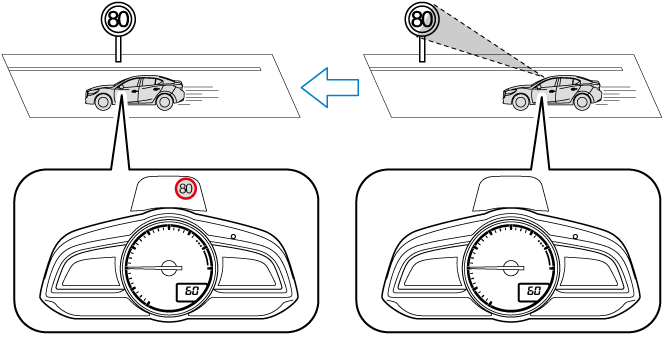
The Traffic Sign Recognition System (TSR) helps prevent the driver from overlooking traffic signs, and provides support for safe driving by displaying traffic signs on the active driving display which are recognised by the Forward Sensing Camera (FSC) or recorded in the navigation system while the vehicle is driven.
If the vehicle speed exceeds the speed limit sign indicated in the active driving display while the vehicle is driven, the system notifies the driver using the indication in the active driving display and a warning sound.
The Traffic Sign Recognition System (TSR) displays the speed limit (including auxiliary signs) and do not enter signs.
-
The Traffic Sign Recognition System (TSR) is not supported in some countries or regions. For information concerning the supported countries or regions, consult an expert repairer, we recommend an Authorised Mazda Repairer.
-
The Traffic Sign Recognition System (TSR) operates only if the navigation system SD card (Mazda genuine) is inserted in the SD card slot. Consult an expert repairer, we recommend an Authorised Mazda Repairer for details.


Always check the traffic signs visually while driving.
The Traffic Sign Recognition System (TSR) helps prevent the driver from overlooking traffic signs and provides support for safe driving. Depending on the weather conditions or problems with traffic signs, a traffic sign may not be recognised or a traffic sign different from the actual traffic sign may be displayed. Always make it your responsibility as a driver to check the traffic signs. Otherwise, it could result in an unexpected accident.


-
The Traffic Sign Recognition System (TSR) does not operate if there is a malfunction in the Forward Sensing Camera (FSC).
-
Under the following conditions, the Traffic Sign Recognition System (TSR) may not operate normally.
-
An object placed on the instrument panel is reflected in the windscreen and picked up by the camera.
-
Heavy luggage is loaded in the luggage compartment or on the rear seat and the vehicle is tilted.
-
The tyre pressures are not adjusted to the specified pressure.
-
Tyres other than standard tyres are equipped.
-
The vehicle is driven on the ramp and surrounding area to or from a rest area or a tollgate on a highway.
-
When surrounding brightness suddenly changes such as when entering or exiting a tunnel.
-
The illumination of the headlights is weakened because of dirt or the optical axis is deviated.
-
The windscreen is dirty or foggy.
-
The windscreen and camera are fogged (water droplets).
-
Strong light is directed at the front of the vehicle (such as backlight or high-beam headlights of on-coming vehicles).
-
The vehicle is making a sharp turn.
-
Strong light reflects off the road.
-
A traffic sign is in a position which makes it difficult to reflect the light from the vehicle's headlights, such as when the vehicle is driven at night or in a tunnel.
-
The vehicle is driven under weather conditions such as rain, fog, or snow.
-
The stored map data for the navigation system is not current.
-
The camera cannot capture a traffic sign's image.
-
A traffic sign is obscured by mud or snow.
-
A traffic sign is concealed by trees or a vehicle.
-
A traffic sign is partially shaded.
-
A traffic sign is bent or warped.
-
A traffic sign is too low or too high.
-
A traffic sign is too bright or too dark (including electronic traffic signs).
-
A traffic sign is too big or too small.
-
There is an object similar to the traffic sign being read (such as another traffic sign or other signs resembling it).
-
-
The Traffic Sign Recognition System (TSR) can be set to inoperable.
Refer to Personalisation Features (Search).




 Read this first
Read this first



















