Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM) System (Some Models)
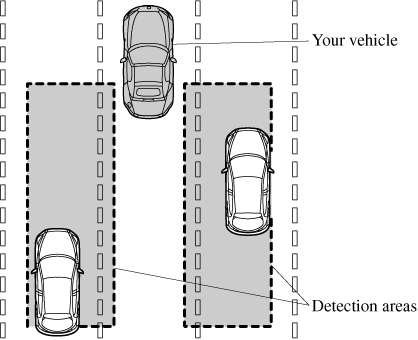
The Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM) is designed to assist the driver in checking the area to the rear of the vehicle on both sides during lane changes by alerting the driver to the presence of vehicles approaching from the rear in an adjacent lane.
The Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM) detects vehicles approaching from the rear while travelling in the forward direction at a speed of 30 km/h (19 mph) or faster and turns on the Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM) warning lights equipped on the door mirrors depending on the conditions. If the direction indicator lever is operated to signal a lane change in the direction in which the Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM) warning light is illuminated, the system warns the driver of a vehicle in the detection area by flashing the Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM) warning light and activating a beep sound.
The detection area on this system covers the driving lanes on both sides of the vehicle and from the rear part of the doors to about 50 m (164 ft) behind the vehicle.
Always check the surrounding area visually before making an actual lane change:
The system is only designed to assist you in checking for vehicles at your rear when making a lane change. Due to certain limitations with the operation of this system, the Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM) warning light may not flash or it might be delayed even though a vehicle is in an adjacent driving lane. Always make it your responsibility as a driver to check the rear.


-
The Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM) will operate when all of the following conditions are met:
-
The ignition is switched ON.
-
The Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM) switch is pressed and the Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM) OFF indicator light in the instrument cluster is turned off.
-
The vehicle speed is about 30 km/h (19 mph) or faster.
-
-
The Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM) will not operate under the following circumstances.
-
The vehicle speed falls below about 25 km/h (15 mph) even though the Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM) OFF indicator light is turned off.
-
The shift lever (manual transmission)/selector lever (automatic transmission) is shifted to reverse (R) and the vehicle is reversing.
-
-
In the following cases, the Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM) OFF indicator light turns on and operation of the system is stopped. If the Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM) OFF indicator light remains illuminated, have the vehicle inspected at an Authorised Mazda Dealer as soon as possible.
-
Some problem with the system including the Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM) warning lights is detected.
-
A large deviation in the installation position of a radar sensor (rear) on the vehicle has occurred.
-
There is a large accumulation of snow or ice on the rear bumper near a radar sensor (rear). Remove any snow, ice or mud on the rear bumper.
-
Driving on snow-covered roads for long periods.
-
The temperature near the radar sensors (rear) becomes extremely hot due to driving for long periods on slopes during the summer.
-
The battery voltage has decreased.
-
-
Under the following conditions, the radar sensors (rear) cannot detect target objects or it may be difficult to detect them.
-
A vehicle is in the detection area at the rear in an adjacent driving lane but it does not approach. The Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM) determines the condition based on radar detection data.
-
A vehicle is travelling alongside your vehicle at nearly the same speed for an extended period of time.
-
Vehicles approaching in the opposite direction.
-
A vehicle in an adjacent driving lane is attempting to pass your vehicle.
-
A vehicle is in an adjacent lane on a road with extremely wide driving lanes. The detection area of the radar sensors (rear) is set at the road width of expressways.
-
-
In the following cases, the activation of the Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM) warning lights and the warning beep may not occur or they may be delayed.
-
A vehicle makes a lane change from a driving lane two lanes over to an adjacent lane.
-
Driving on steep slopes.
-
Crossing the summit of a hill or mountain pass.
-
The turning radius is small (making a sharp turn, turning at intersections).
-
When there is a difference in the height between your driving lane and the adjacent lane.
-
Directly after pressing the Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM) switch and the system becomes operable.
-
-
If the road width is extremely narrow, vehicles two lanes over may be detected. The detection area of the radar sensors (rear) is set according to the road width of expressways.
-
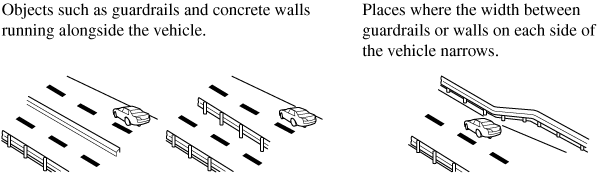
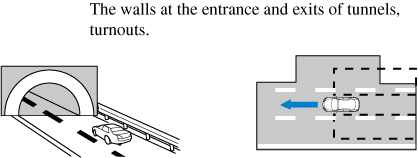
The Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM) warning lights may turn on in reaction to stationary objects on the road or the roadside such as guardrails, tunnels, sidewalls, and parked vehicles.
-
A Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM) warning light may flash or the warning beep may be activated several times when making a turn at a city intersection.
-
Turn off the Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM) while pulling a trailer or while an accessory such as a bicycle carrier is installed to the rear of the vehicle. Otherwise, the radar’s radio waves will be blocked causing the system to not operate normally.
-
In the following cases, it may be difficult to view the illumination/flashing of the Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM) warning lights equipped on the door mirrors.
-
Snow or ice is adhering to the door mirrors.
-
The door glass is fogged or covered in snow, frost or dirt.
-
-
The system switches to the Rear Cross Traffic Alert function when the shift lever (manual transmission) or the selector lever (automatic transmission) is shifted to the reverse (R) position.
Refer to Rear Cross Traffic Alert (RCTA) (Search).




 Read this first
Read this first



















